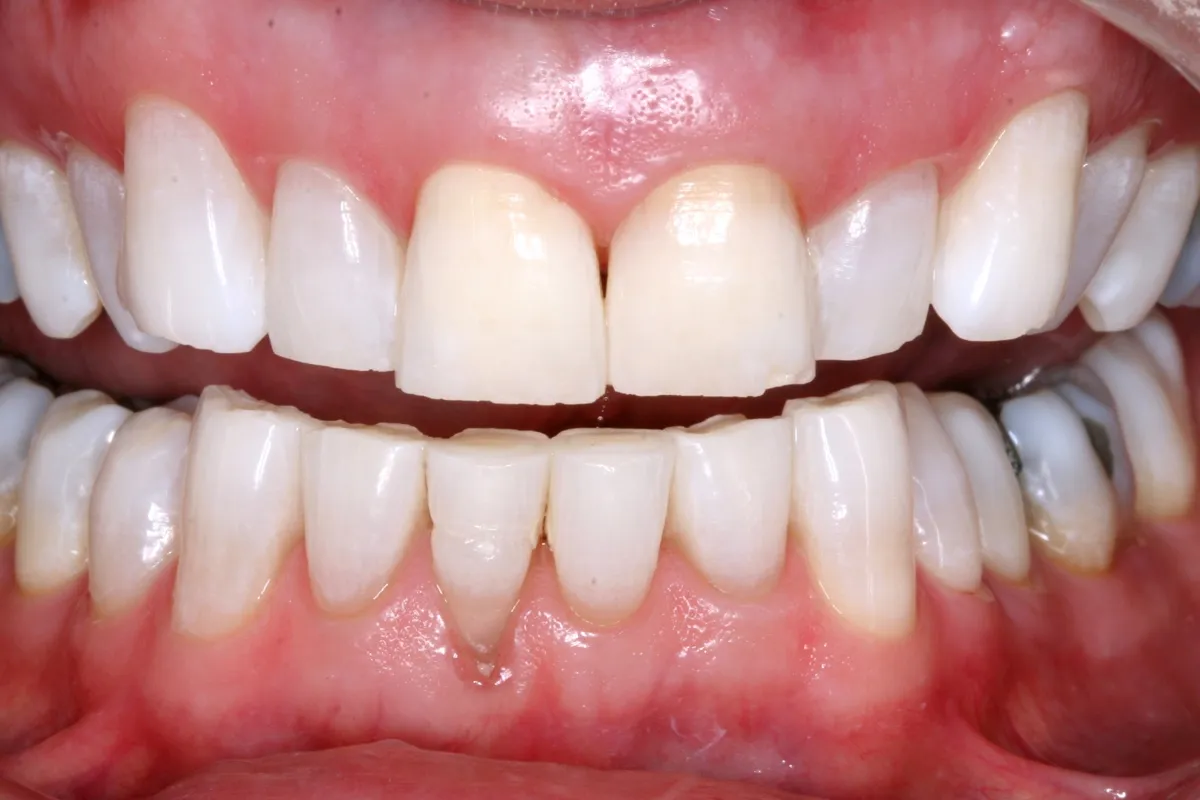
Understanding Teeth Whitening and Gum Health
Teeth whitening has become a popular cosmetic procedure, promising a brighter and more confident smile. However, it’s crucial to understand the process and its potential impact on your gums. The goal is to achieve a dazzling smile without compromising the health of your gums, which play a vital role in overall oral hygiene. This guide explores the science behind teeth whitening, the causes of gum discoloration, preventive measures, safe techniques, and post-whitening care. It’s essential to approach teeth whitening with knowledge and caution, ensuring both aesthetics and dental health are prioritized. Properly understanding the processes involved, from the chemical reactions to the potential side effects, can help you make informed decisions and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.
The Science Behind Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening primarily involves the use of bleaching agents, most commonly hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These agents penetrate the enamel and dentin of your teeth, breaking down the stains that cause discoloration. The effectiveness of the whitening process depends on the concentration of the bleaching agent, the duration of its contact with the teeth, and the type of stains present. The breakdown of stain molecules causes the teeth to appear lighter, but it’s a complex chemical process. This process doesn’t affect the natural color of your teeth, only the stains that have accumulated. The duration of the process may vary according to the methods implemented to whiten your teeth, thus, it is extremely important to be aware of these procedures.
How Whitening Agents Work
Whitening agents work by releasing oxygen molecules that react with the stain molecules embedded within the tooth’s enamel. These oxygen molecules break the bonds of the stain molecules, causing them to disperse and making the teeth appear brighter. Different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide are used in various whitening products, such as those used at home or those applied by a dentist. The higher the concentration, the faster the whitening process, but the greater the risk of side effects, such as gum irritation and sensitivity. Proper application and guidance are essential to ensure safe and effective results. Understanding how these agents interact with the tooth structure is crucial for minimizing potential adverse effects and maximizing the benefits of the treatment.
Why Gums Can Turn White
One of the most common concerns associated with teeth whitening is the potential for gums to turn white. This discoloration is a sign that the bleaching agent has come into contact with the soft tissues of the gums. The whitening agents, especially when used at high concentrations, can irritate or even burn the gums. This is because the gums are much more sensitive than the enamel of the teeth. When the bleaching agent comes into contact with the gums, it can cause the proteins in the gum tissue to denature, leading to a temporary whitening effect. The whiteness indicates a mild chemical burn, which usually resolves itself within a few days if the exposure is limited. However, prolonged or excessive exposure can cause more severe damage, thus, precautions should be observed.
Causes of Gum Discoloration During Whitening
Chemical Burns from Whitening Agents

Chemical burns are the most direct cause of gums turning white during teeth whitening. This occurs when the bleaching agent comes into direct contact with the gum tissue. High concentrations of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide are more likely to cause burns, which can range from mild irritation to more severe damage. The chemical reaction denatures the proteins in the gum tissue, resulting in a white appearance and potential discomfort. The severity of the burn depends on factors such as the concentration of the bleaching agent, the duration of exposure, and the individual’s sensitivity. Proper techniques and protective measures, such as using custom-fitted trays and applying a gingival barrier, can help prevent chemical burns and ensure the safety of the procedure.
Irritation from Ill-Fitting Trays
Ill-fitting whitening trays can also lead to gum irritation and discoloration. When trays don’t fit properly, the bleaching agent can leak out and come into contact with the gums, causing irritation and potential burns. This is more common with over-the-counter whitening kits that use generic trays. Custom-fitted trays, made by a dentist, provide a better fit and minimize the risk of leakage. The tray needs to cover the teeth closely but not touch or irritate the gums. If the tray is too big or too small, the bleaching agent can seep out and cause the gums to turn white, leading to sensitivity and discomfort. Proper tray fit is therefore an essential step in the teeth whitening process to protect gum health and achieve optimal results.
Pre-existing Gum Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing gum conditions, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, are at higher risk of experiencing gum irritation during teeth whitening. The compromised gum tissue is more sensitive and susceptible to damage from bleaching agents. The inflammation associated with these conditions makes the gums more vulnerable, leading to a greater chance of discoloration and discomfort. Before undergoing any teeth whitening procedure, it’s essential to address and treat any existing gum issues. Consulting a dentist to ensure your gums are healthy will help minimize the risk of complications and ensure a safe and effective whitening experience. Healthy gums are the foundation of a successful teeth whitening process.
Preventive Measures Before Whitening

Consulting Your Dentist
Before starting any teeth whitening treatment, consulting with your dentist is the most important step. A dentist can assess your oral health, identify any pre-existing conditions, and determine if teeth whitening is appropriate for you. They can evaluate the health of your gums and teeth, screen for cavities, and ensure that your gums are in good condition. Your dentist can also recommend the most suitable whitening method based on your needs and expectations. Professional guidance helps to minimize risks and maximize results. They can also provide custom-fitted trays, monitor your progress, and provide guidance on how to manage any side effects. Consulting with your dentist is a great step towards a brighter smile.
Evaluating Gum Health
A thorough evaluation of your gum health is crucial before proceeding with teeth whitening. Your dentist will examine your gums for signs of inflammation, recession, or other issues. If your gums are inflamed or infected, whitening treatment is best postponed until the condition is treated. Healthy gums provide a protective barrier, which is essential to prevent the bleaching agent from irritating or burning the soft tissues. Your dentist might recommend a professional cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. This cleaning will create a healthier environment for the whitening process. Addressing gum health issues ensures a safer and more effective whitening experience, and it also helps maintain overall oral health.
Choosing the Right Whitening Method
Selecting the right teeth whitening method depends on your individual needs, preferences, and oral health. There are various options available, including over-the-counter products and professional treatments. Over-the-counter options, such as whitening strips and trays, are often more affordable. They can be a good starting point for mild discoloration, but they may not be as effective as professional treatments. Professional whitening procedures, such as in-office bleaching, are performed by a dentist and use higher concentrations of bleaching agents. These treatments provide faster and more dramatic results. Your dentist will help you choose the method that is best suited for you. Your decision should be guided by your dentist’s assessment, your desired outcome, and any sensitivity concerns. Choosing the right method is a key factor in achieving a brighter smile safely and effectively.
Safe Whitening Techniques and Products
Over-the-Counter Whitening Options
Over-the-counter teeth whitening products are readily available and can be a convenient option for mild tooth discoloration. These products include whitening strips, trays, toothpastes, and gels. Whitening strips are easy to use and apply directly to the teeth, while trays are filled with a whitening gel and worn for a specified time. Whitening toothpastes contain mild abrasives that can help remove surface stains, but they do not typically contain bleaching agents. When using over-the-counter products, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to minimize the risk of gum irritation. Always check the product for an ADA (American Dental Association) seal of approval, which ensures that the product has been tested for safety and effectiveness. Start by using the product for the shortest recommended time to assess how your teeth and gums respond, and consult with your dentist if you experience any adverse effects.
Professional Teeth Whitening Procedures
Professional teeth whitening procedures offer a more powerful and controlled approach to achieving a brighter smile. These procedures are performed by a dentist or a dental professional in a clinical setting. In-office bleaching uses high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, which can produce significant whitening results in a single visit. The dentist protects your gums with a barrier before applying the whitening agent to your teeth. Another option is custom-fitted whitening trays that are made based on the shape of your teeth. These trays can be used at home with a professional-strength whitening gel. These trays fit perfectly and minimize any potential for the whitening agent to irritate the gums. Professional procedures typically provide faster and more dramatic results compared to over-the-counter options. Your dentist will monitor your progress, address any sensitivities, and ensure your safety throughout the process.
Home Remedies and Their Effectiveness
Some home remedies are claimed to whiten teeth, but their effectiveness and safety can vary. These remedies include brushing with baking soda, using activated charcoal, and oil pulling with coconut oil. While baking soda can act as a mild abrasive to remove surface stains, excessive use can damage tooth enamel. Activated charcoal can also remove surface stains, but it may not whiten teeth effectively and can be abrasive. Oil pulling involves swishing oil around the mouth. Some proponents claim this removes bacteria and promotes oral health, but there is limited scientific evidence to support its teeth-whitening benefits. These remedies may not be as effective as professional whitening treatments or over-the-counter products. Always discuss any home remedies with your dentist before trying them to avoid potential harm to your teeth and gums.
Post-Whitening Care and Maintenance
Soothing Irritated Gums

After teeth whitening, it’s common to experience some gum irritation, especially if your gums came into contact with the bleaching agent. If your gums turn white or become sore, there are several steps you can take to soothe them. Rinse your mouth with warm salt water several times a day, as this helps reduce inflammation and promote healing. Avoid using harsh toothpastes or mouthwashes that can further irritate your gums. Consider using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth, which often contains ingredients like potassium nitrate to reduce sensitivity. Applying a small amount of vitamin E oil directly to your gums can also help soothe and speed up healing. If the irritation is severe or persistent, contact your dentist for advice and possible treatment. These steps will help ease discomfort and promote the healing process.
Maintaining a Bright Smile
Maintaining a bright smile after teeth whitening involves several key practices. First, avoid foods and drinks that can stain your teeth, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries. If you consume these items, brush your teeth soon after to remove stains. Avoid smoking and using tobacco products, as they are major contributors to tooth discoloration. Regular brushing and flossing are essential for removing plaque and surface stains. Use a whitening toothpaste to help maintain your bright smile. Consider using a straw when drinking staining beverages to minimize contact with your teeth. Regular dental checkups and professional cleanings are also important to maintain your results. Following these practices will help prolong the effects of teeth whitening and keep your smile shining brightly.
When to Seek Professional Help
While minor gum irritation after teeth whitening is common and usually resolves itself, there are times when you should seek professional help. If your gums experience severe pain, excessive swelling, or bleeding, it is important to consult your dentist. If your gums turn significantly white and the discoloration persists for more than a few days, this could indicate a chemical burn that requires professional care. If you experience tooth sensitivity that lasts for more than a few days or becomes very intense, inform your dentist. Any signs of infection, such as pus or fever, require immediate dental attention. Your dentist can assess the situation, provide appropriate treatment, and ensure that any complications are properly managed. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice if you have concerns about your gum health or your teeth after whitening.